The first patent for a drip irrigation system was issued in Israel in 1963. Given the growing shortage of drinking water around the world and its measurable reduction, also the gradual disappearance and drainage deep into the planet, and as a result, the constant increase in its cost, the advantages of the drip system are undeniable. Drip irrigation avoids excessive water usage and as a result, reduces the cost of final products, which is of no small importance nowadays.
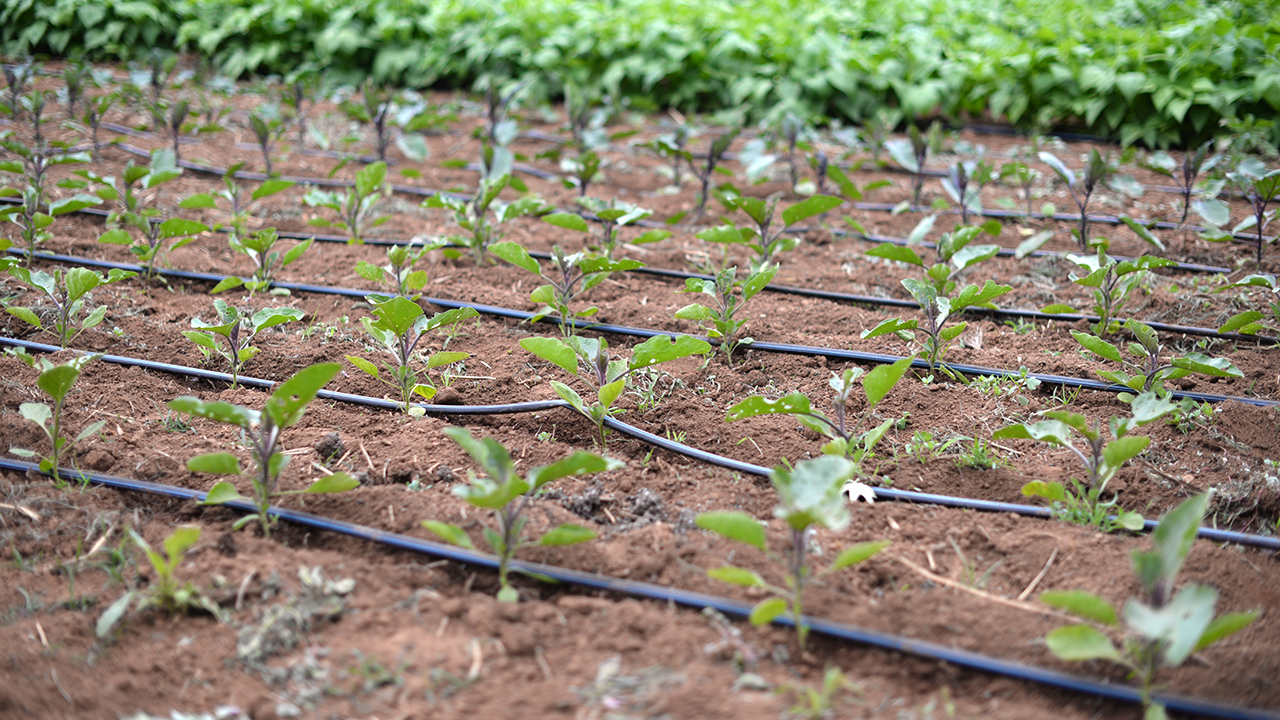
With drip irrigation, water is delivered to the plant root through the dosing units called emitter or dripper. This method saves water due to the lack of evaporation of the fluid delivered through the pipes. As a rule, duration and intensity of watering sessions are regulated based on the settings adjusted by the Firm's specialists - suppliers. Considering that each culture requires an individual approach and individual amount of water, the irrigation system justifies itself in growing the crops that are sensitive to irrigation regime and most importantly, to soil moisture.
This system has proven to be an enormous success and paid well off in the countries with an arid climate. These are African countries, Israel, Egypt and Australia. The drip irrigation system has been put to good use in Caucasian countries, namely, in Azerbaijan and Georgia. It has been proven itself to be indispensable in many countries thanks to effective watering and the feasibility to raise many crops, including the exotic ones. The drip irrigation system is distinguished from other irrigation techniques by dosed feeding of water directly into the root system. Apart from watering, this system, by way of concurrent feeding-in of fertilizers, provides the plant root with necessary micro-nutrients required for proper growth, being beneficial both in terms of crop quality and quantity. Mixing of the fertilizers with water is done in the fertigation unit.
Crops can be raised in moderately saline soils with the help of drip irrigation technologies. This method of irrigation leads to the washing of the salts from the area around the drippers, which is very beneficial for the plants, as the root system in the watered point easily absorbs minerals, nutrient substances and moisture from the leached area.
Drip irrigation techniques are divided into three main categories: subsurface, surface and above-surface drip irrigation.
In the case of subsurface irrigation, the drip pipes are laid at a depth of 10 to 40 cm. For surface drip irrigation the drip pipes are laid in the furrows along planting rows. For above-surface drip irrigation, the drip pipes are hanged at a certain height from the ground.
Above-surface and on-surface irrigation systems are low-budget solutions, but subsurface irrigation has more advantages. Due to direct access to the root system, the subsurface irrigation method saves a significant amount of water and ensures the opportunity to continue other works during irrigation or immediately after it along with the safety of the systems.
A drip irrigation system includes:
- filter unit
- water intake unit
- fertigation unit (fertigation - a method of fertilizer application in which fertilizer is incorporated within the irrigation water by the drip system).
- main pipeline
- drip lines and distributing pipeline
- pressure regulator
- water meter
- a controller that ensures the absolute control over the watering process, including the timing and duration of watering, and water volume.
Advantages:
- Up to 95% of the feed water is uptaken by irrigated crops.
- The plants are provided with moisture in the right amount and at the right time.
- In comparison with surface watering, water consumption is reduced by 40-50%.
- Fertilizer consumption is reduced by 50% compared to surface watering.
- The risk of plant diseases is significantly reduced since the leaves always remain dry.
- Thanks to the automation of the watering and plant nutrition, labor costs are saved.
Installation of a drip irrigation system (DIS) calls for a greater focus on details, as it is a complex process. It requires to take into account the following aspects: how filters will be installed and what types of filtration are needed; exact choice of pipe diameters; which types of pipes should be used in the main pipeline; selection of drippers taking into account the planting schemes, soil composition, specifics of the culture, etc.
Drip irrigation is one of the most scrupulous watering methods, which requires a careful selection of specialists. Because, with great probability, it will be impossible to do the substandard works over again. As a result, you will have to assemble the system from scratch. Saving on components, professional design, and installation (specialists) will result in expenses greater than the mere cost of a drip irrigation system.
Applications of drip irrigation systems and their specifics.
Drip irrigation systems are used both on open (fields and gardens) and protected ground (greenhouses) for the cultivation of vegetable crops, trees, shrubbery, and fruits.
It is appropriate to use the drip irrigation system in the following cases where it is impossible to use other methods:
- if the land is very steep (45 degrees or higher) or has a very challenging terrain;
- in the regions with strong and constant winds, as well as prolonged droughts;
- in the regions with limited local water sources;
- in the regions with poor fertility topsoil and in the soils with too weak or too strong hygroscopic properties (hygroscopy is the ability of the soil to co-opt water or absorb moisture from the air);
- in the regions with the soil prone to salinization;
- in cases where the irrigation water contains water-soluble salts.